1) Where does Yoga come from?
Yoga is a traditional physical and mental discipline that has its roots in India. Although the West discovered this practice in the 1960s, according to researchers, the first forms of yoga would have taken place between 10,000 and 5,000 BC.
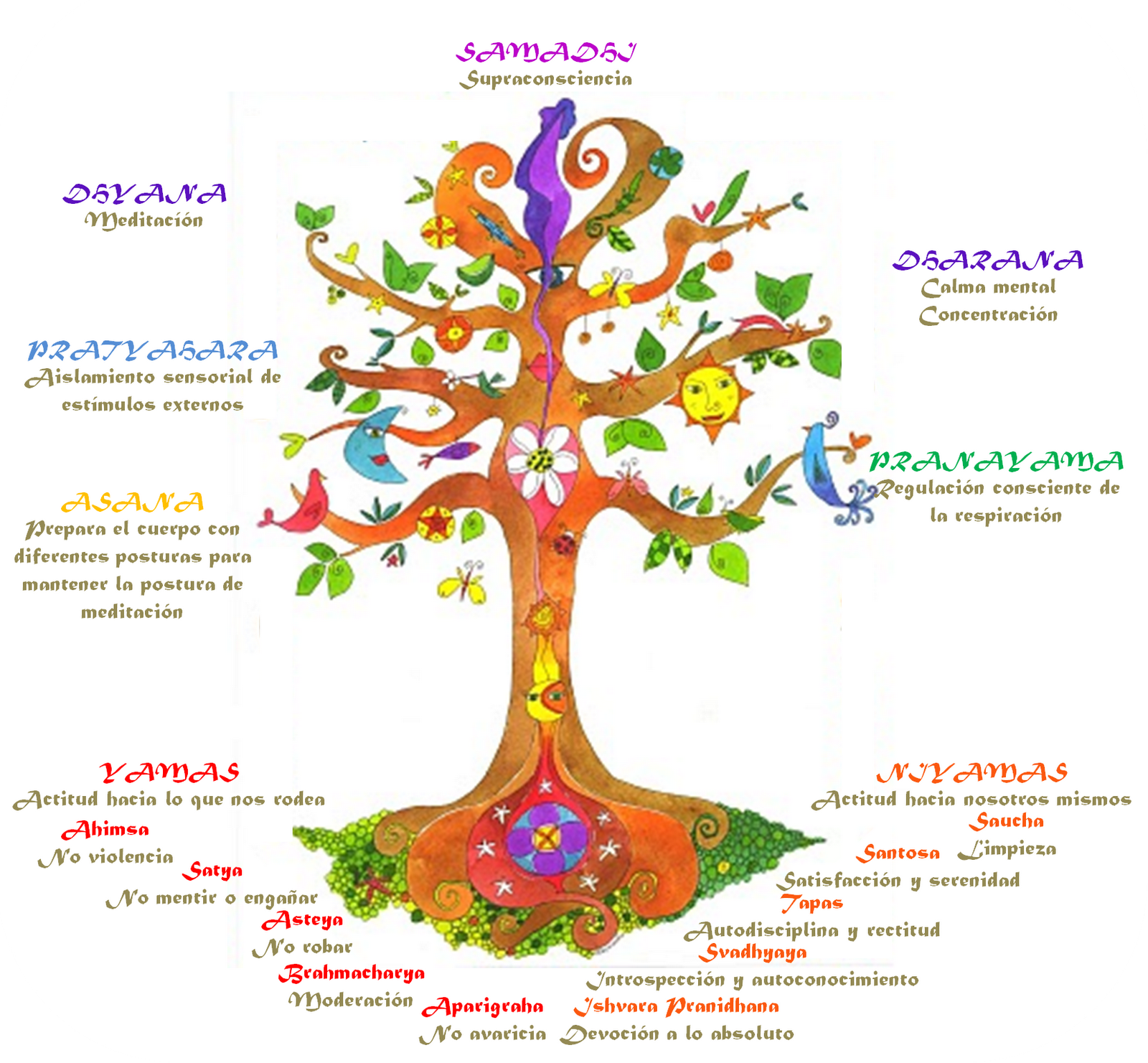
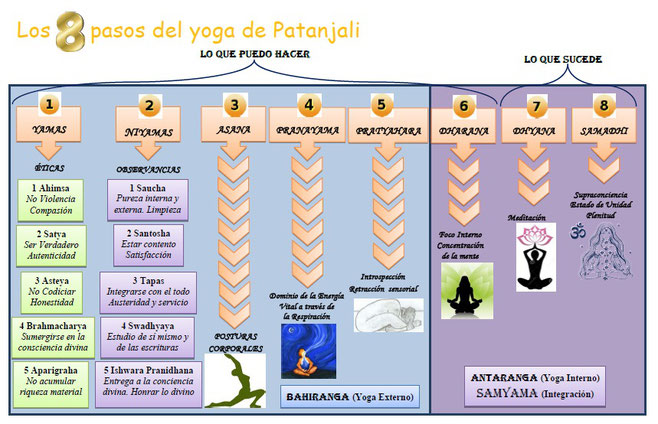
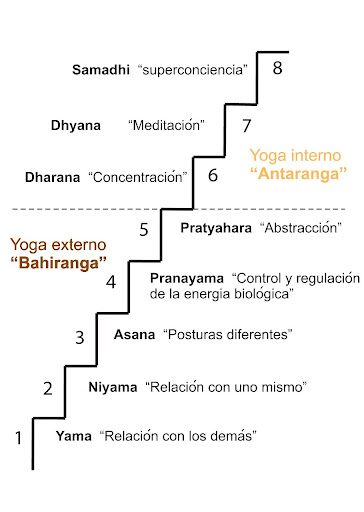
Maharishi Mahest, focusing on meditation, was the one who popularized this practice. Meanwhile, Swami Sivananda gained fame with his system of Yoga, which was based on five principles:
- breathing (pranayamas),
- asanas (yoga poses),
- relaxation,
- positive thoughts,
- meditation.
2) What are the types of Yoga?
Although there are many types of Yoga, they all have the same purpose. Therefore, here are some types of this discipline:
- HATHA: It is a good introduction to get started in Yoga, as it is the basis of the other physical Yoga styles. It links breathing with movement, the balancing of opposites and the cleansing and revitalization of the body’s energy channels. It is a slow and deep practice of postures.
- KUNDALINI or YOGA OF CONSCIOUSNESS: its central technique is to awaken the kundalini (the energy found at the base of the spine). It is a style of spiritual Yoga, which involves mudras, mantras, candles and incense. Consecutive series of exercises are performed in order to achieve a goal, the so-called Kriyas. Classes include relaxation and meditation.
- POWER: In this case, one moves from one posture to another in a fluid way, doing intense cardiovascular work that requires strength, endurance and flexibility. It is a dynamic, physically demanding and vigorous practice.
- VINYASA: It means the link between breathing and movement. Vinyasa synchronizes each movement with an inhalation, retention or exhalation, which makes for fluid movements.
- WOMB YOGA: It is a Yoga that nurtures women emotionally, spiritually, physically and mentally. It also works on healing and activation.
- ANTI-STRESS YOGA: Includes exercises that relieve pain and improve mood, creating space in our body and mind for energy to circulate better.
- MINDFULNESS: Through this practice, we become aware of the different facets of our experience in the present moment. We learn to be aware of how we move, how we feel and how we react to each moment of life.

Yoga class in the Botanic Garden of Barakaldo
3) Fundamental texts of Yoga
- The Bhagavad Gita: it is a short summary of Hindu doctrines, which establishes the main currents of Yoga.
- The Yoga-Sutra of Patanyali: these are ancient foundational texts of Yoga.
- The Hatha-Yoga-Pradypika: it is considered the oldest text on Hatha Yoga.
4) Yogic nutrition
In general, Yoga practitioners try to reduce the amount of food they eat. They try to have a Mediterranean diet to maintain an adequate weight. They do what is necessary to acquire a general well-being, both physical and mental. With the practice of Yoga, many of them eliminate meat and other foods that are not adequate for the human organism.
5) Philosophy
Yoga is not only physical exercise, but a discipline of millenary origin that has evolved in the western world. Through Yoga techniques, one can understand the purpose of life and live in a state of compassion and openness both psychically and spiritually.

6) Health
Practicing this discipline improves health and leads to a more balanced life. It also fills its practitioners with good energy and happiness. Physical exercise is especially aimed at the health of our spine. Breathing increases energy, recharges the body and facilitates the control of emotions and mind. Relaxation frees us from tension and stress. A light diet, based on natural foods, keeps the body light and flexible.
By practicing positive thoughts, negative thoughts disappear and meditation silences the mind.
SOURCE: https://yogarivas.com/6-cosas-que-no-sabias-sobre-el-yoga/


Recent Comments